Energy Systems Catapult’s (ESC) Living Lab has reached a new milestone, with 1,000 household across the UK joining since its launch in 2017.
The Living Lab serves as a real-world test environment designed to develop solutions that help reduce daily carbon emissions and comprises a wide variety of property types and family demographics.
More than 660 households are situated in England, with the West Midlands (14%) and South East (9%) among the regions with the highest numbers, Scotland has more than 300, Wales 100 and the Northern Ireland recently added its first 14 homes.
Some properties are equipped with up to 10 smart and low carbon energy devices – ranging from heat pumps, solar PV, electric vehicle chargers, battery storage or smart heating – while other homes only having a gas boiler and no low carbon devices.
Homes are connected by a digital integration platform to ESC’s trial curators, ensuring the Living Lab is digitally open, interoperable and scalable.
Moreover, this allows new technologies to be tested in real world conditions, working with more common technologies such as smart meters or internet of things (IoT) devices.
As the chart below shows, more than half are equipped with smart heating solutions. Almost all the houses (89%) have a gas boiler, with just 11% have a heat pump. One in five generation power from rooftop solar PV.
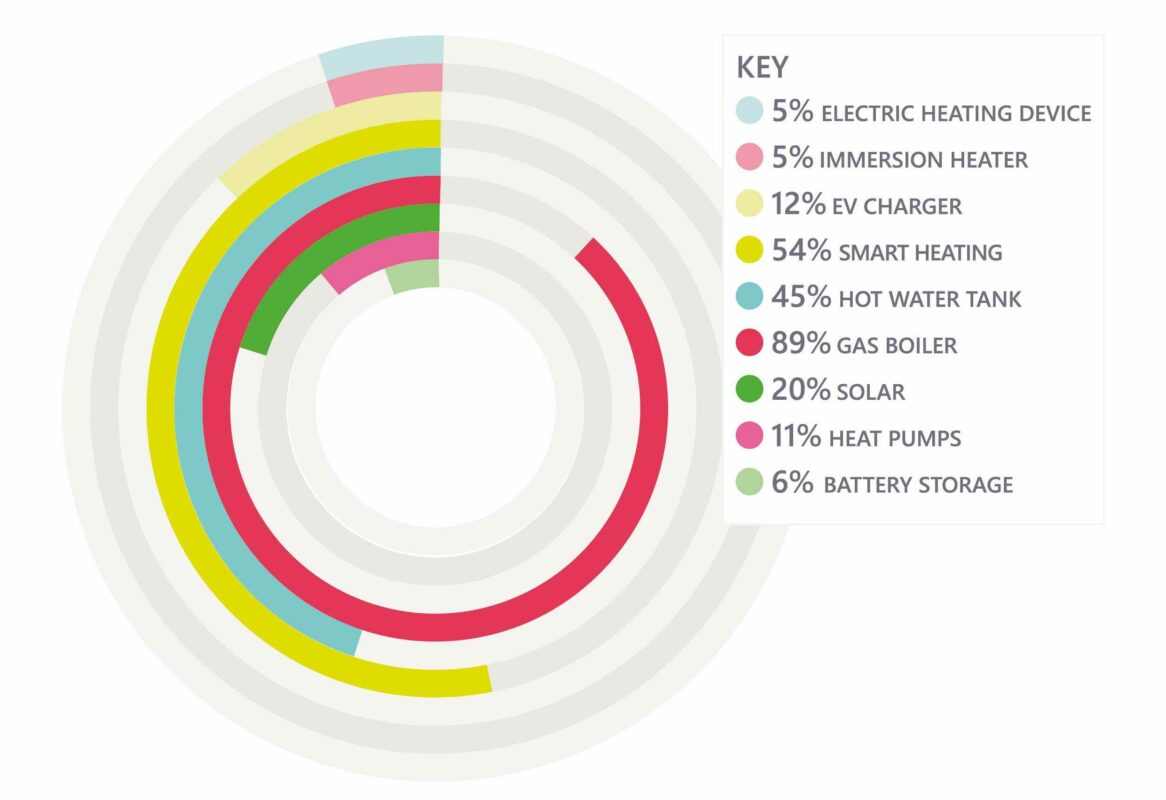 Percentage proportion of Living Lab homes with different technology types. Image: Energy Systems Catapult.
Percentage proportion of Living Lab homes with different technology types. Image: Energy Systems Catapult.
“It’s great to reach this milestone number of homes taking part in our Living Lab. We’re building a diverse community of residential properties of all shapes and sizes, and with different heating technologies installed, to give us a unique insight into our changing energy demands throughout the net zero transition,” said Rebecca Sweeney, business lead at Living Lab.
“This insight into our evolving energy habits – and how consumers and the market respond to new technologies – will be crucial to encourage innovation and help us design products and services for the future energy system.”
ESC has run a number of trials using the Living Lab including an autonomous digital energy assistant designed by Amp X and a cloud-based Digital Integration Platform from SysMech.