National Grid has used a new web-based platform to dispatch ancillary services using battery storage in the first example of the new system being implemented across its reserve products.
First revealed in December 2017 as part of the transmission system operator’s Product Roadmap For Frequency Response and Reserve, the Ancillary Services Dispatch Platform (ASDP) is intended to allow National Grid greater access to new technology types, enhancing flexibility across energy sources.
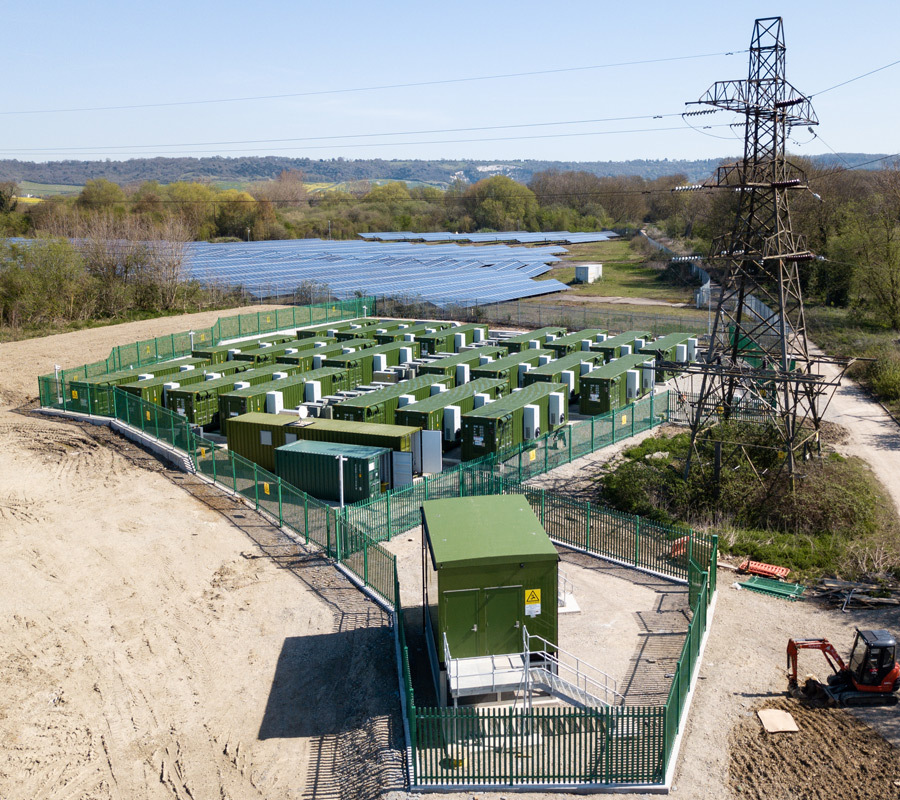
It was used on 19 July to procure stored power from Zenobe Energy, which supplied 24MWh over a 30 minute period from a 50MW facility.
Zenobe Energy, which counts former National Grid chief executive Steve Holliday as its non-executive chairman, was until recently known as Battery Energy Storage Solutions (BESS). It is not known how the company was selected to take part in the dispatch pilot, as Zenobe did not respond to requests for clarification from Current±
However, it would have utilised some of its 63MW portfolio of battery sites to deliver the total dispatched volume. The firm’s sites include the 29MW site at Aylesford in Kent and the 20MW site at Claredown in Essex, as well as the 9.6MW Kings Barn battery in West Sussex.
It also counts five battery sites co-located with solar farms within its list of assets, adding a further 3.85MW to battery storage capacity.
While National Grid would not comment further, it is expected to continue to utilise the ASDP following the successful dispatch of services using battery storage.
It will be used to aggregate and summarise the reserve volumes available to the control room, coordinate despatch across a large number of connected assets and providers, and provide a route for automated monitoring of delivery.
In December, the grid operator said it would roll the platform out further into the Short Term Operatoing Reserve (STOR) market, with the ambition to replace the existing despatch system with ‘a flexible, scalable and secure platform’.