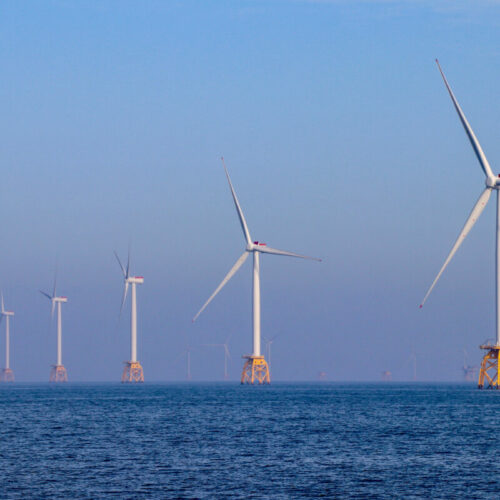
Latest data from National Grid ESO (ESO) has shown that 52% of Britain’s electricity in July came from low carbon sources.
This includes electricity generated from wind, solar, and nuclear.
Low carbon generation peaked on 15 July at 3pm producing 86% of the Britain’s electricity.
🌬 A gusty month meant wind made up 29% of generation in July, with 52% of electricity coming from zero carbon sources 🍃 At 3pm on 15 July, the use of renewables peaked at 86%, enabling electricity to be generated at a monthly carbon intensity low of 39 gCO2/kWh ⚡ See more 👇
— National Grid ESO (@NationalGridESO) August 2, 2023
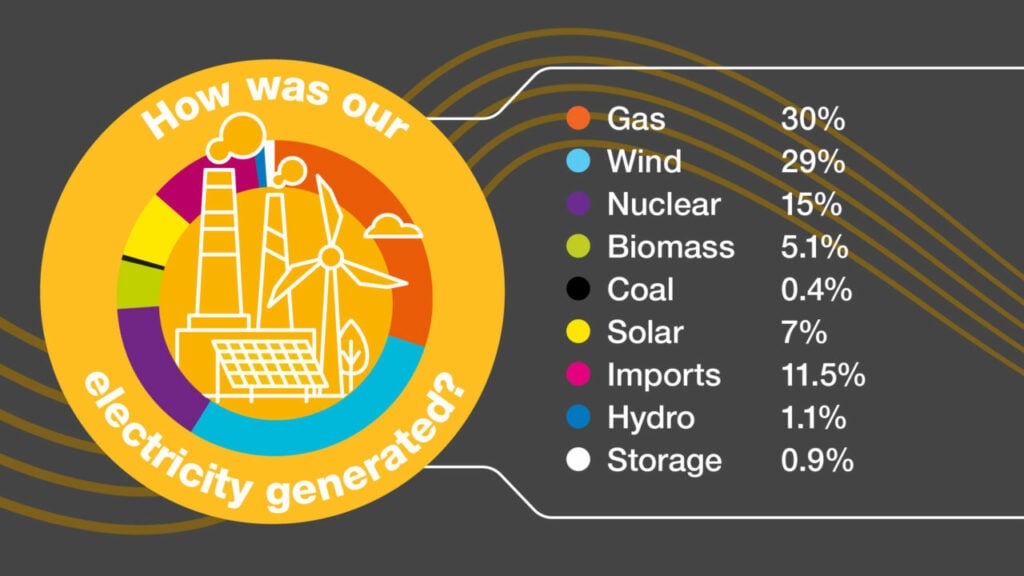
Gas was the largest single electricity provider at 30% followed closely by wind (29%), before nuclear (15%), solar (7%) and biomass (5.1%).
The increasing share renewables have in Britain’s electricity mix translates to cheaper prices for consumers in the long-term.
As demonstrated in last month’s generation statistics, wind is particularly prominent in lowering energy prices; for example, in the week beginning 20 March 2023, wind generated between 46% and 56% of the UK’s energy mix for three days, resulting in a day ahead price low of £12/MWh on 25 March.
The statistics from ESO follow a release from the Department of Energy Security and Net Zero (DESNZ) which showed that renewables generated a record 41.5% (135TWh) of electricity in the UK last year.
Current± publisher Solar Media is hosting the third edition of its Wind Power Finance & Investment Summit Europe in London this 19-20 September. The conference will focus on investment strategies, alleviating bottlenecks, and which countries and technologies are the most exciting ahead as the industry sets to expand to help reach 2030 targets. Packed with industry leaders representing financiers, investors, developers, government departments and more this is the leading conference for decision makers in the European wind industry. More information, including how to attend, can be read here.